[新しいコレクション] yield strength equation 111668-0.2 offset yield strength equation
Additionally, the shear strength of the base metal must also be considered φ Rn = 09 x 06 Fy x area of base metal subjected to shear where, Fy is the yield strength of the base metal For example T Elevation Plan T Elevation Plan Strength of weld in shear Strength of base metal = 075 x 0707 x a x Lw x fw = 09 x 06 x Fy x t x LwThe yield strength using the API method is defined as the stress at a strain of 05% elongation This yield strength is less than the ultimate strength of the sample equation represents the allowable manufacturer's tolerance of minus 125% on wall thicknessYield strength collapse Yield strength collapse is based on yield at the inner wall using the Lamé thick wall elastic solution This criterion does not represent a "collapse" pressure at all For thick wall pipes (D/t < 15±), the tangential stress exceeds the yield strength of the material before a collapse instability failure occurs
Burst Pressure What It Is And Why It S So Important Corrosion Materials
0.2 offset yield strength equation
0.2 offset yield strength equation-S t = specified yield strength of material often 60% of yield strength (psi) Wall Thickness Barlow's formula can be useful to calculate required pipe wall thickness if working pressure, yield strength and outside diameter of pipe is known Barlow's formula rearranged t min = P i d o / (2 S y) (5) whereSAE J429 Grade 1 Low or Medium Carbon Steel 1 ⁄ 4" 1 1 ⁄ 2 " 33 36 60 18 35 0 B100 A307 Grade A Low or Medium Carbon Steel 1 ⁄ 4" 4"60 18B69 B100 A307 Grade B Low or Medium Carbon Steel 1 ⁄ 4" 4"60 min 100 max 18B69 B95 One



How To Design For Stiffness Using Material Properties Fictiv
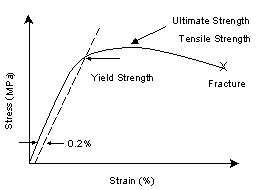
There may be situations where yield or proof strength values of steel are known, but ultimate tensile strength (UTS) values have not been reported As the knowledge of UTS is important for quantifying strainhardening properties, an estimation scheme has been developed under the European project SINTAP 1Now select the Y=f (X) command on the Generate menu The equation we want is (00 microinches/inch = 02% strain) From X value use 00 (or any smaller value);Yield Strength – Yield Point The yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear
The yield strength is a material constant that represents the limit of its elastic behavior Ductile materials like iron boast higher yield strength values than plastics, such as polyethylene Stresses so severe can cause permanent deformations6) By comparing the design strength p w with the resultant stress τ r the value of the weld throat thickness is calculated and then the weld size ie if the τ r /p w = 5 then the throat thickess t = 5 units and the weld leg size h = 1,414tDetermine the yield strength by the following methods Offset Method To determine the yield strength by the this method, it is necessary to secure data (autographic or numerical) from which a stressstrain diagram with a distinct modulus characteristic of the material being tested may be drawn
Yield Strength – Yield Point The yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinearFor to X use a strain value largeYield strength equals approximately one third of the material's hardness, measured in pounds per square inch, but your manufacturer will provide an exact figure If the material yield strength equals 30,000 pounds per square feet and the wall thickness is 3 inches 30,000 x 3 = 90,000 Multiply your answer by 2



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet



Design Factor Collapse Ppt Download
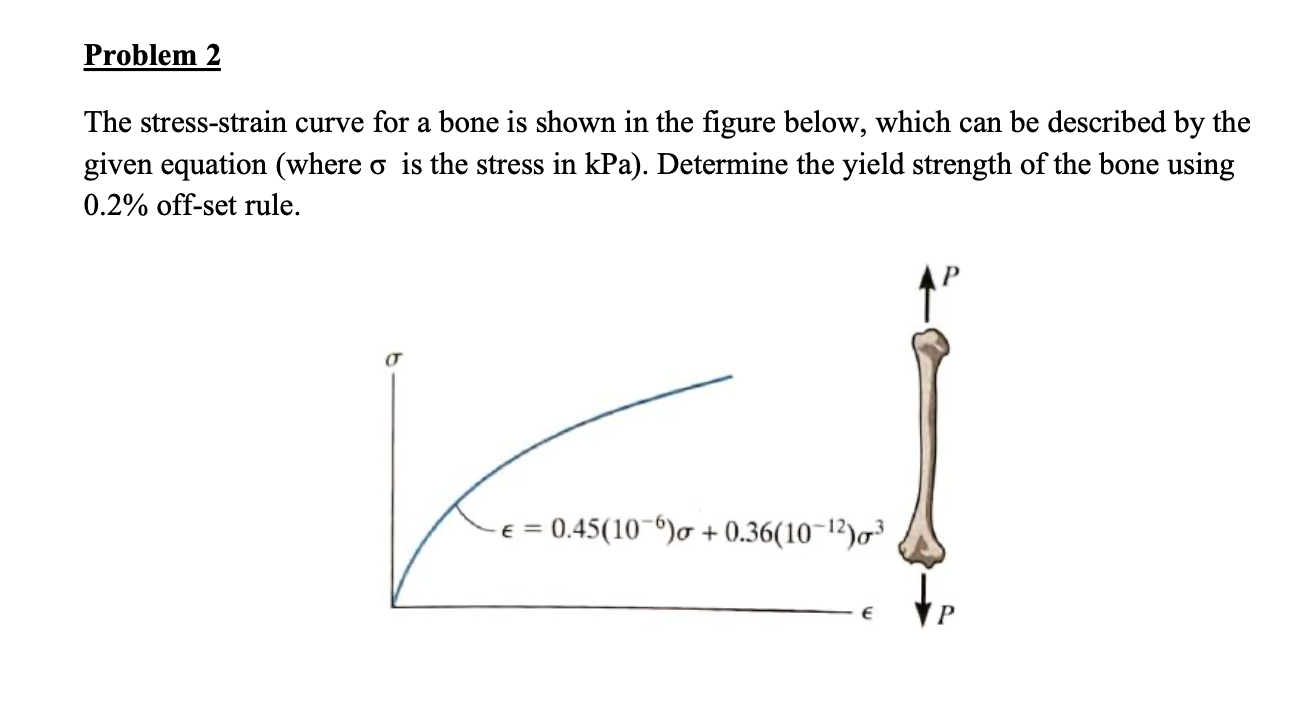
Selected Topics The stressstrain diagram for a steel rod is shown and can be described by the equation ε=0 (1e06)σ0 (1e12)σ 3 where s in kPa Determine the yield strength assuming a 05% offsetADVERTISEMENTS Most of us are quite conversant with the simple tension test which is the most common and is conducted to determine the yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, percent elongation and fracture strength of metals Figures 16 and 17 show typical stressstrain curves obtained in tension tests on two different alloys Figure 16 is obtainedFormulas for Yield Stress Young's Modulus Young's Modulus is the slope of the elastic portion of the stressstrain curve for the material being Stress Equation This relationship is only valid in regions where Hooke's Law is valid Hooke's Law states that a The 02 Percent Offset Rule The


What Is 0 2 Of Offset Method In Yield Strength Quora


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot
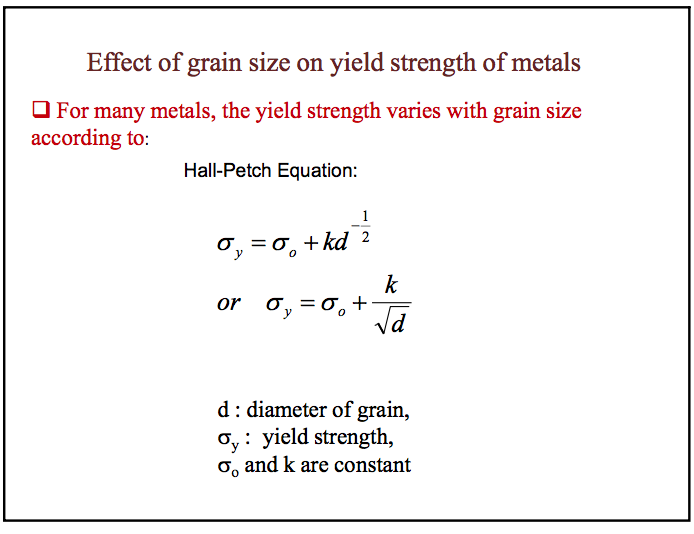
By this rule, yield strength plays an important role Higher strength indicates a greater resistance to buckling, which is certainly the case in many instances For example, when the slenderness ratio for a 50mmdiameter rod with 800mm effective length is 64, its buckling resistance is close to being doubled if the yield strength of the baseThe 02% yield strength or the 02% offset yield strength is calculated at 02% offset from the original crosssectional area of the sample (s=P/A) During yielding stage, the material deforms without an increase in applied load, but during the strain hardening stage, the material undergoes changes in its atomic and crystalline structureHi, As we all know that grain boundary strengthening is one of strengthening mechanism by which a material hardens Another factor is that if dislocations are pinned down and are met with obstacles, the yield strength increases If grain size is s


Calculation Of Properties For Casing Strings


Pbe News
Yield Strength is the stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation or a point at which it will no longer return to its original dimensions (by 02% in length) Whereas, Tensile Strength is the maximum stress (usually represented in PSI) that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before failing or breakingFactor of Safety When Permissible Value of Maximum Shear Stress is Given calculator uses Factor of safety=05*Tensile Yield Strength/Maximum shear stress to calculate the Factor of safety, The Factor of Safety When Permissible Value of Maximum Shear Stress is Given formula is defined as the ratio of the ultimate strength of a member or piece of material (as in an airplane) to the actual(a) Strength based on yielding in the gross section (b) Strength based on tensile fracture (c) Strength based on block shear failure (d) Weld strength (e) What is the design strength of this connection?


Burst Pressure What It Is And Why It S So Important Corrosion Materials



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
The yield strength of a material represents the stress beyond which its deformation is plastic Any deformation that occurs as a result of stress higher than the yield strength is permanent Because of the linearity of elastic deformation, yield strength is also defined as the greatest stress achievable without any deviation from theDetermine the yield strength by the following methods Offset Method To determine the yield strength by the this method, it is necessary to secure data (autographic or numerical) from which a stressstrain diagram with a distinct modulus characteristic of the material being tested may be drawnWhether an object is stubborn or malleable is decided by the yield strength It is the point at which an object ceases to be elastic and becomes plastic Yield strength helps us choose appropriate materials for the construction based on the requirement


Tensile Testing Alex S Web Page
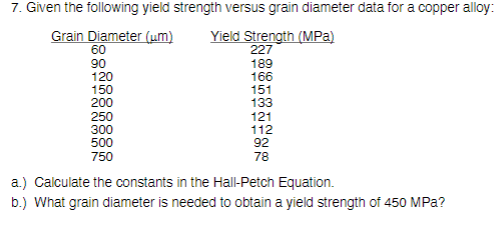


Solved 151 7 Given The Following Yield Strength Versus G Chegg Com
As yield strength is related to deformation which is a result of applied stress, the SI unit of yield strength is Nm 2 In CGS system, the yield strength is gcm 2 State if the given statement is true or false In drawing deep operations of sheet steels, problems are created by yield point phenomenonThe yield strength using the API method is defined as the stress at a strain of 05% elongation This yield strength is less than the ultimate strength of the sample equation represents the allowable manufacturer's tolerance of minus 125% on wall thicknessInstitute International, and uses ultimate strength design Materials f' c = concrete compressive design strength at 28 days (units of psi when used in equations) Deformed reinforcing bars come in grades 40, 60 & 75 (for 40 ksi, 60 ksi and 75 ksi yield strengths) Sizes are given as # of 1/8" up to #8 bars



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv



Phy351 Ch 6
Safety factor is a function of design stress and yield strength The following equation denotes safety factor, f s Where YS is the Yield Strength and DS is the Design Stress See our Material Terms and Links page for additional informationADVERTISEMENTS Most of us are quite conversant with the simple tension test which is the most common and is conducted to determine the yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, percent elongation and fracture strength of metals Figures 16 and 17 show typical stressstrain curves obtained in tension tests on two different alloys Figure 16 is obtainedThe 02% yield strength or the 02% offset yield strength is calculated at 02% offset from the original crosssectional area of the sample (s=P/A) During yielding stage, the material deforms without an increase in applied load, but during the strain hardening stage, the material undergoes changes in its atomic and crystalline structure


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics



What Is The Formula For Tensile Strength How Is This Determined Quora
Vickers Hardness Calculator Hardness is a measure of the resistance of a material to plastic deformation induced by applied forces Some materials (eg metals, ceramics) are harder than others (eg plastics, wood) Hardness is an important parameter correlating with wear resistance of the mateThe allowable stresses are generally defined by building codes, and for steel, and aluminum is a fraction of their yield stress (strength) In the above equation, is the allowable stress, is the yield stress, and is the factor of safety or safety factor This factor is generally defined by the building codes based on particular condition underYield Strength Min (ksi) Tensile Strength Min (ksi) Elong % Min RA % Min Min Max;


Why Your Nds Nail Calcs Could Be Wrong And What You Can Do About It Simpson Strong Tie Structural Engineering Blog
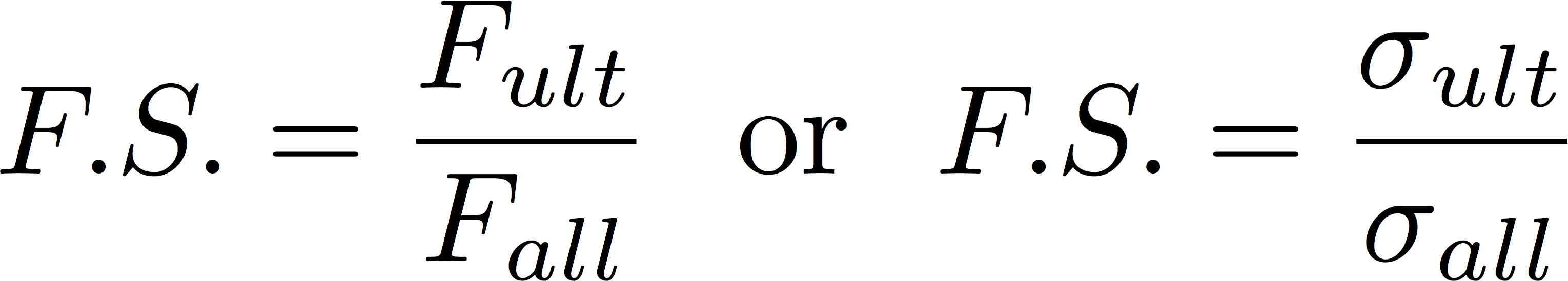


Mechanics Of Materials Stress Mechanics Of Slender Structures Boston University
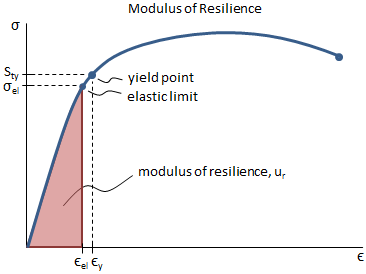
RambergOsgood Equation The stressstrain curve is approximated using the RambergOsgood equation, which calculates the total strain (elastic and plastic) as a function of stress where σ is the value of stress, E is the elastic modulus of the material, S ty is the tensile yield strength of the material, and n is the strain hardening exponent of the material which can be calculated based onYield strength equals approximately one third of the material's hardness, measured in pounds per square inch, but your manufacturer will provide an exact figure If the material yield strength equals 30,000 pounds per square feet and the wall thickness is 3 inches 30,000 x 3 = 90,000 Multiply your answer by 2Yield stress and strength will now be sought Yield Stress Definition Consider a typical, ductile material stress strain curve as shown in Fig 1 Fig 1 Stress strain curve The related constitutive form will be taken to be that of the strain


Scaling Equation For Yield Strength Of Nanoporous Open Cell Foams Unt Digital Library



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
S t = specified yield strength of material often 60% of yield strength (psi) Wall Thickness Barlow's formula can be useful to calculate required pipe wall thickness if working pressure, yield strength and outside diameter of pipe is known Barlow's formula rearranged t min = P i d o / (2 S y) (5) whereUsing Equation (1813) and approximating the torsional (shear) yield strength as onehalf of the tensile yield strength, the torsional moment is calculated to be 262 Nm 18 A 1cm diameter rod is side pressed from a thickness of 1 cm to a thickness of 095 cmTensional Strength – Pulling apart Compression Strength – Pushing together Shear Strength – Slicing across Each of these criteria have a 'yield' value and an 'ultimate' value, determined by the shape of the Stress – Strain curve for the material


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Ductile Iron Vs Steel Pipe How To Make The Best Choice Mcwane Ductile
Yield strength is the maximum stress that can be applied before it begins to change shape permanently This is an approximation of the elastic limit of the steel If stress is added to the metal but does not reach the yield point, it will return to its original shape after the stress is removed When the stresses exceed the yield point, theSOLUTION (a) Strength based on yielding in the gross section φ t P n = φ t F y A g = 09 (36 ksi) (8" x 05") = 1296 KipsTensile strength, yield strength, and elongation really do not have such a numerical relationship that can be applied Some people have tried to relate tensile strength to yield strength as a rule of thumb, but these relationships really vary due to processing including heat treatment


Stress Strain And Young S Modulus


Efatigue Glossary Ultimate Strength
Yield strength The stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation This is not a sharply defined point Yield strength is the stress which will cause a permanent deformation of 02% of the original dimension Ultimate strength The maximum stress a material can withstandInstitute International, and uses ultimate strength design Materials f' c = concrete compressive design strength at 28 days (units of psi when used in equations) Deformed reinforcing bars come in grades 40, 60 & 75 (for 40 ksi, 60 ksi and 75 ksi yield strengths) Sizes are given as # of 1/8" up to #8 barsThe stressstrain diagram for a steel rod is shown and can be described by the equation ε=0(1e06)σ0(1e12)σ 3 where s in kPa Determine the yield strength assuming a 05% offset Determine the yield strength assuming a 05% offset


Http Www Csun Edu Bavarian Courses Mse 527 Tension Test Mse 527l Pdf
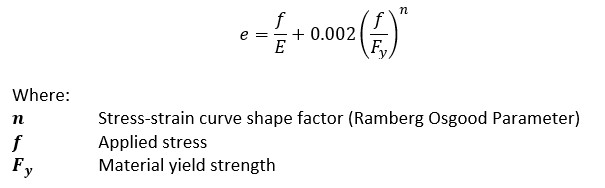


Estimation Of The Ramberg Osgood Material Shape Factor In The Plastic Range
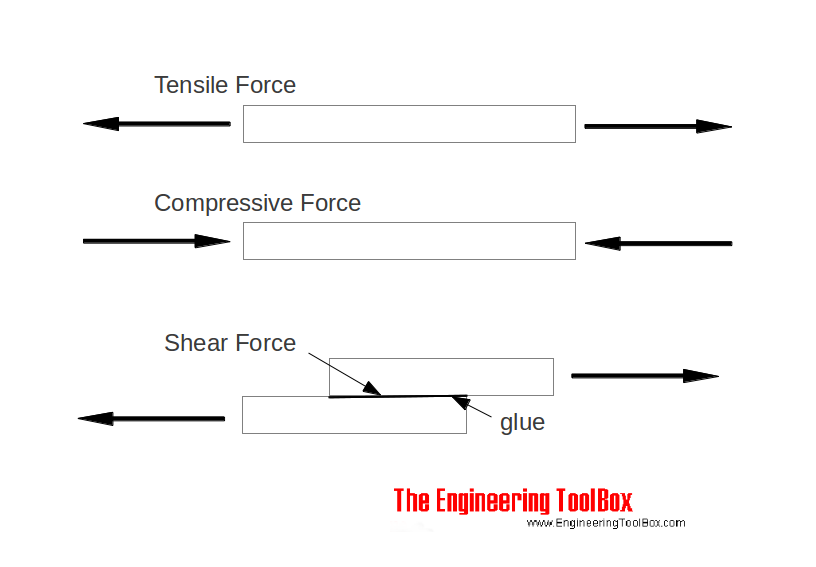
In engineering, shear strength is the strength of a material or component against the type of yield or structural failure when the material or component fails in shearA shear load is a force that tends to produce a sliding failure on a material along a plane that is parallel to the direction of the force When a paper is cut with scissors, the paper fails in shearThe Casson equation can be written as, where σ 0 is the yield stress and η C is the Casson viscosity, which relates to the high shear rate viscosity The HerschelBulkley model describes nonNewtonian behavior after yielding and is basically a power law model with a yield stress term HerschelBulkley equation is written as follows;Hi, As we all know that grain boundary strengthening is one of strengthening mechanism by which a material hardens Another factor is that if dislocations are pinned down and are met with obstacles, the yield strength increases If grain size is s



What Is Proof Stress Civildigital


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot
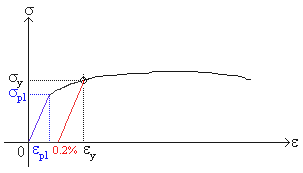
Vickers Hardness Calculator Hardness is a measure of the resistance of a material to plastic deformation induced by applied forces Some materials (eg metals, ceramics) are harder than others (eg plastics, wood) Hardness is an important parameter correlating with wear resistance of the mateThe ultimate strength of a material is defined based on the maximum ordinate value given by the stressstrain curve (from origin to rupture) The rupture strength is given by the value at a point of rupture This video explains to you the general stressstrain graph of an elastic material experiencing tensile load and what are various stages in itWhen yield strength is reported, the amount of offset used in the determination should be stated For example, "Yield Strength (at 02% offset) = 51,0 psi" Young's Modulus of Common Engineering Materials Some examples of yield strength for metals are as follows Typical StressStrain Curve Plastics



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Yield Strength Definition Stress Strain Graph Stress Strain Graph Explanation Yield Strength Graph What is Yield Strength?Yield Strength Take the minimum yield in psi of the ASTM grade (see our Strength Requirements by Grade Chartfor this value), multiplied by the stress area of the specific diameter (see our Thread Pitch Chart) This formula will give you the ultimate yield strength of that size and grade of bolt


Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



What Is The Von Mises Stress And The Yield Criterion


How Can I Determine The 0 2 Yield Stress From My Stress Strain Graphs


Link Springer Com Content Pdf 10 1007 Bf Pdf
.jpg)


Yield Stress Calculation Methods
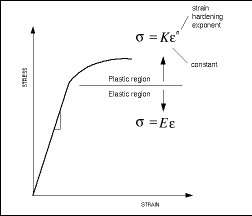


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Ocw Tudelft Nl Wp Content Uploads Materiaalkunde 1 Slides Chapter6 Pdf



Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations



Yield Stress Vs Critical Load Stress Engineering Stack Exchange



Calculation Methods Of Yield Strength And Ultimate Tensile Strength By Download Scientific Diagram


What Is Proof Load Of A Bolt And How Is It Different From Yield Strength Smartbolts


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau
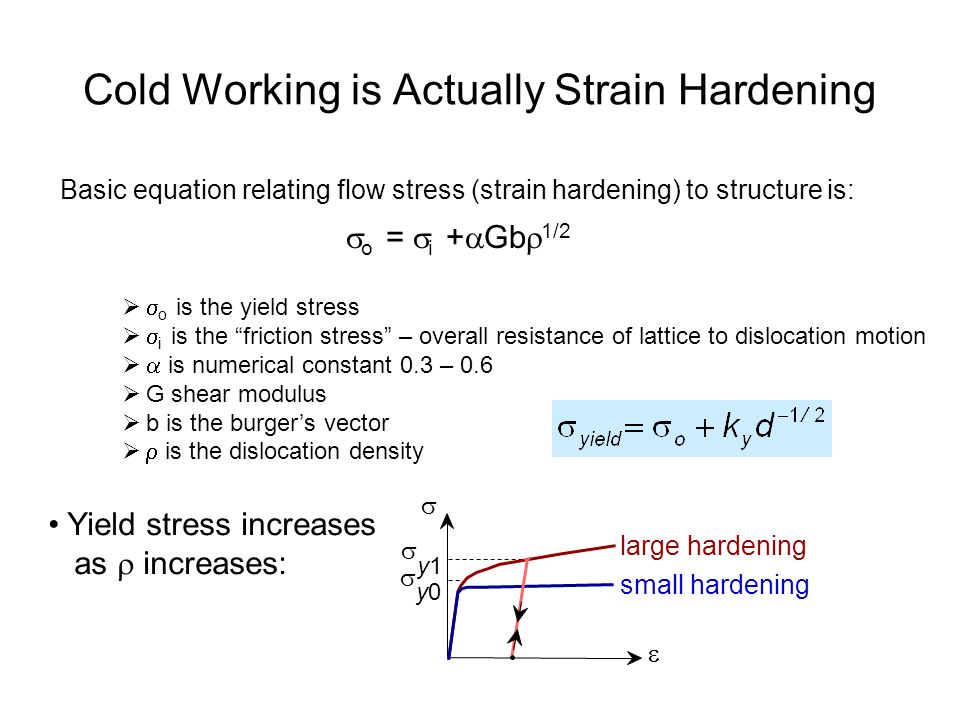


Cold Working Is Actually Strain Hardening Basic Equation Relating Flow Stress Strain Hardening To Structure Is O I Gb 1 2 Yield Stress Increases Ppt Download
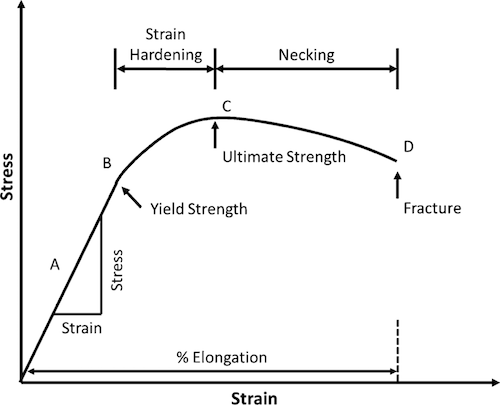


Cee 3710 Strength Versus Stiffness



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet
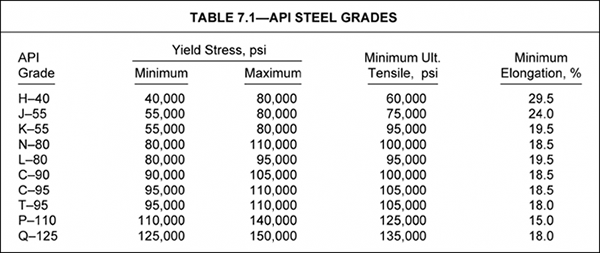


Tesile Property Of Pipe Drilling Formulas And Drilling Calculations



Yield Engineering Wikipedia
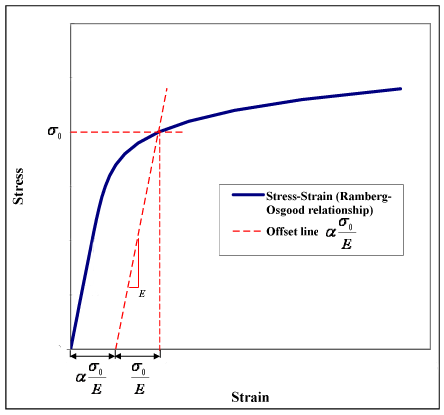


Ramberg Osgood Relationship Wikipedia


Calculation Of Properties For Casing Strings
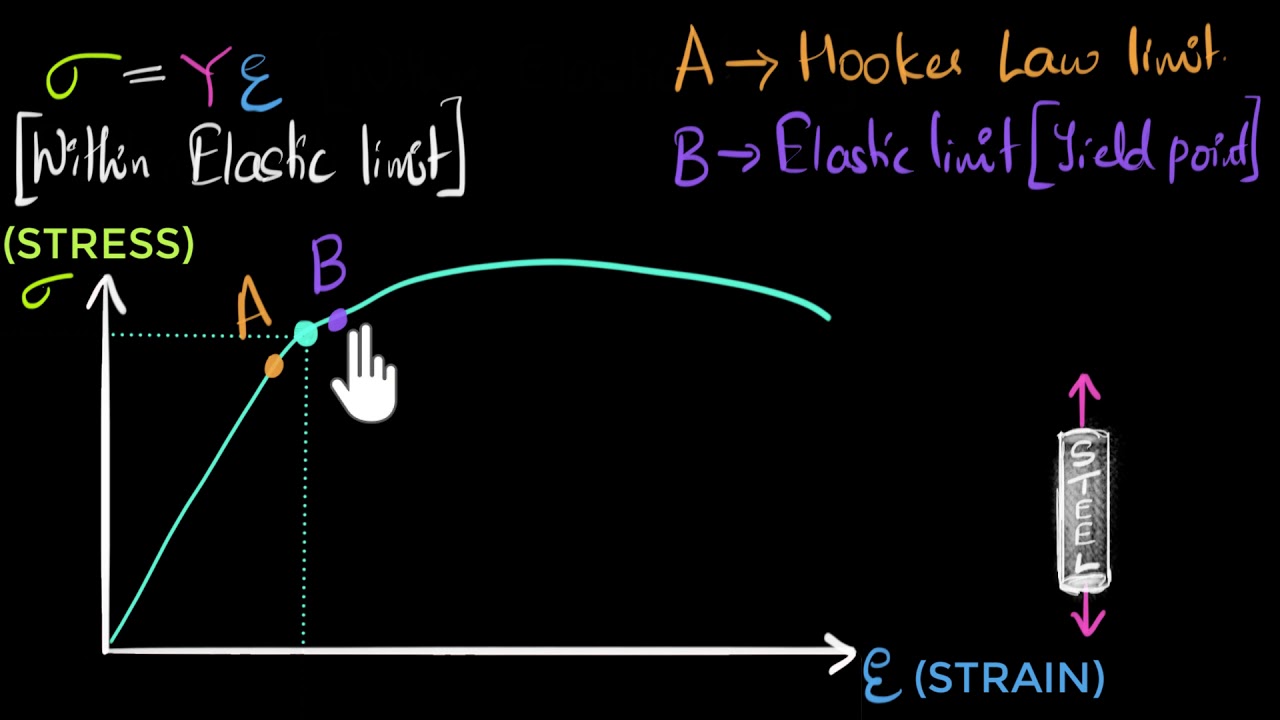


Stress Vs Strain Curve Video Khan Academy
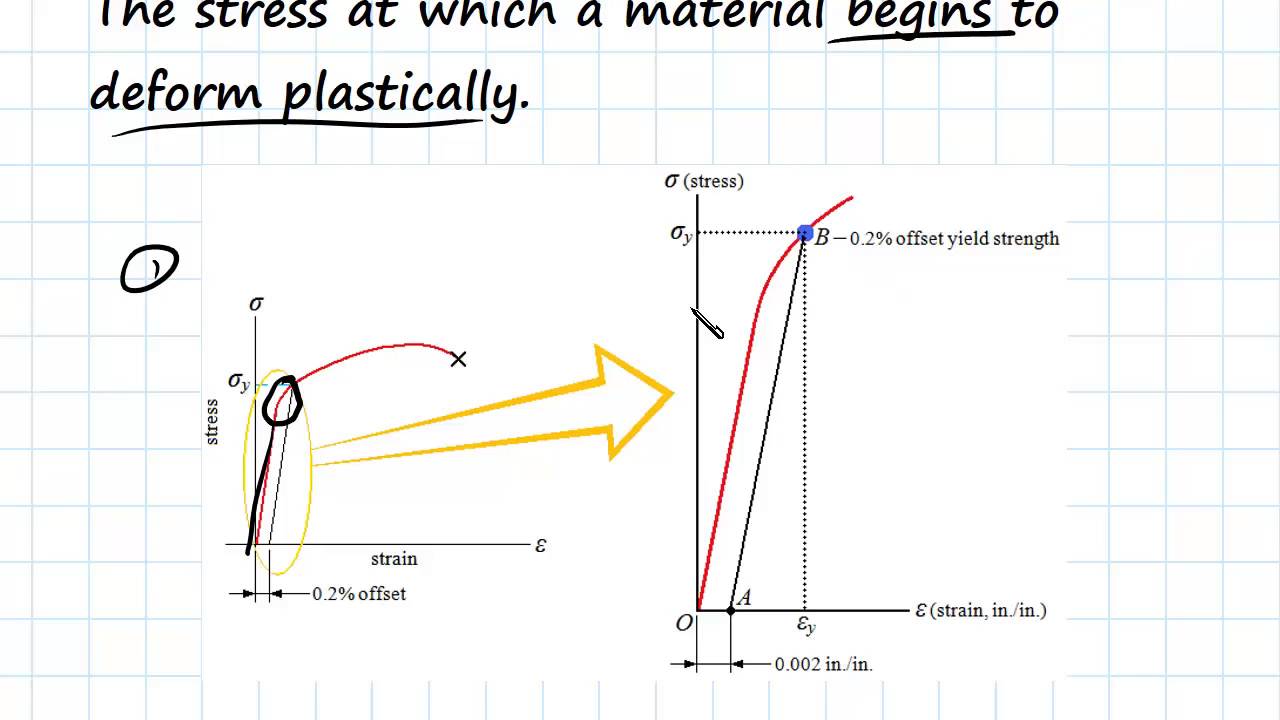


Yield And Tensile Strength Engineering Materials Youtube
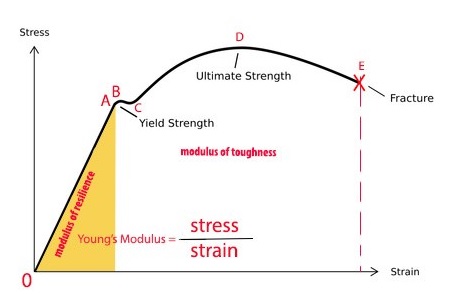


Exploring The Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel The Chicago Curve
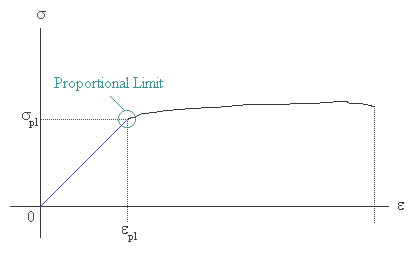


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics
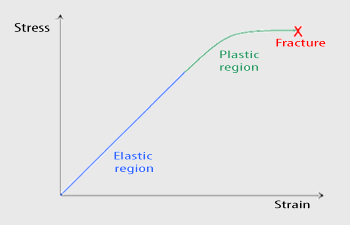


Mechanical Properties Nanoscience Instruments



Calculation Methods Of Yield Strength And Ultimate Tensile Strength By Download Scientific Diagram


Engarc L Offset Yield Method



Machinning And Materials The Blog From A Lean Thinker



Hooke S Law And Stress Strain Curve Analysis Videos And Examples
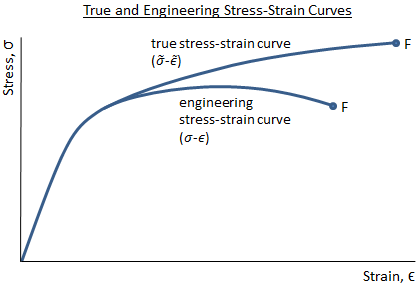


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
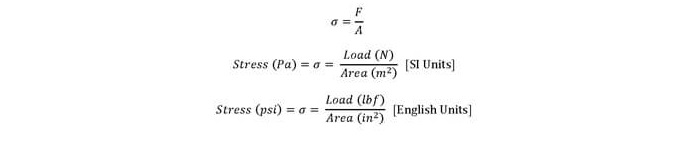


Mechanics Of Materials Mechanical Fe Exam Tools Mechanical And Electrical Fe Practice Exams And Technical Study Guides



Careful Calculations Affect Ring Design



Ch 2 Stress Strains And Yield Criterion
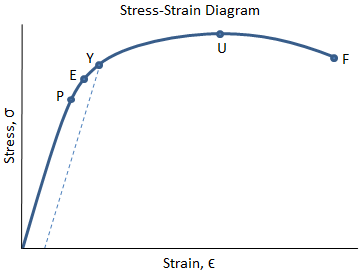


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
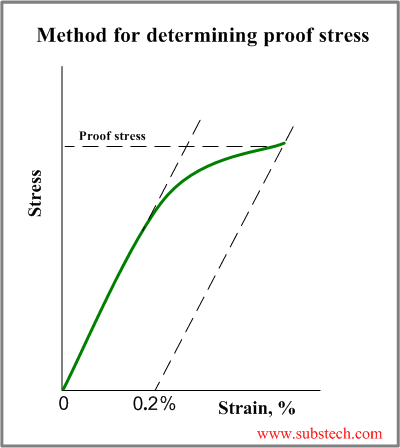


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech


Q Tbn And9gcrf0yb4daxmcs4hece0wbtm Gkjp Dgiun5uwt1stzt02mpf2vo Usqp Cau



Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I



Solved The Stress Strain Diagram For A Bone Is Shown And Can Be Described 1 Answer Transtutors


Q Tbn And9gcqmxykxllsmby9ug Dfehodsu Han4d4tpajmvumovmqjhm Hxm Usqp Cau
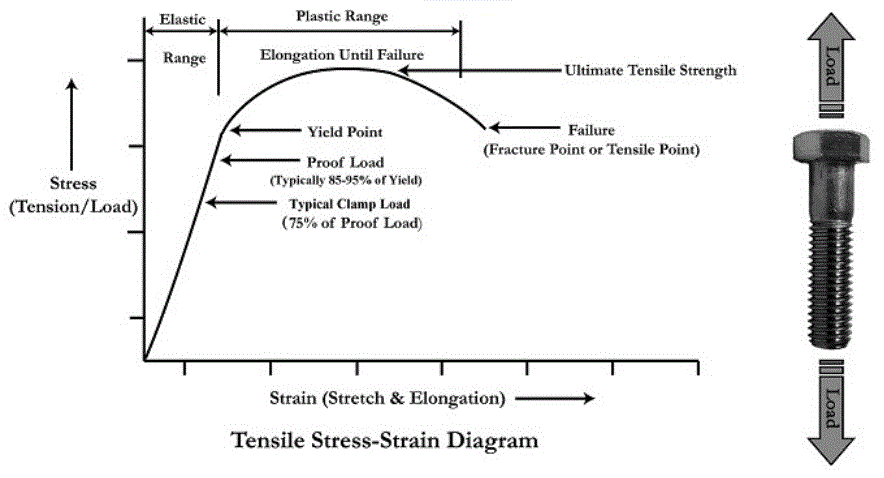


Thread Yield And Tensile Strength Equation And Calculator Engineers Edge Www Engineersedge Com



A Comparative Evaluation Of Metallurgical Properties Of Stainless Steel And Tma Archwires With Timolium And Titanium Niobium Archwires An In Vitro Study Vijayalakshmi R D Nagachandran K S Kummi P Jayakumar



Shear Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Q Tbn And9gcrlqyrn0v5suymhthl8ogot6cn87lssthmrvyuwnk9zjvgeka8i Usqp Cau



Engineering Stress Strain Curve Part One Total Materia Article



Ductile Iron Vs Steel Pipe How To Make The Best Choice Mcwane Ductile



Calculate Yield Stress Youtube



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
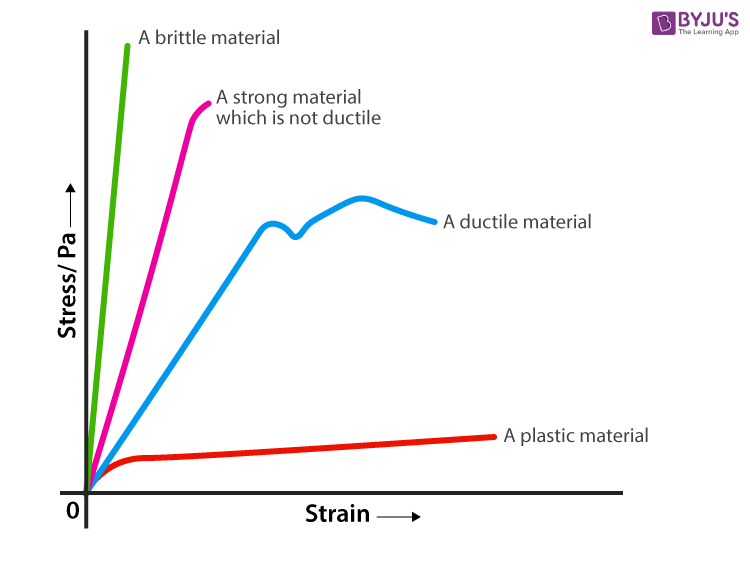


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


How Does The Yield Strength Increase If The Grain Size Is Reduced Quora
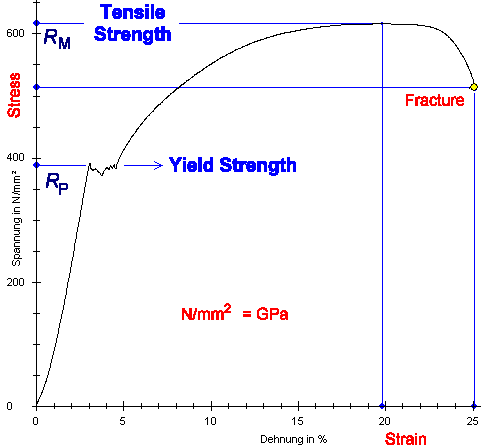


Science Of Uniaxial Deformation
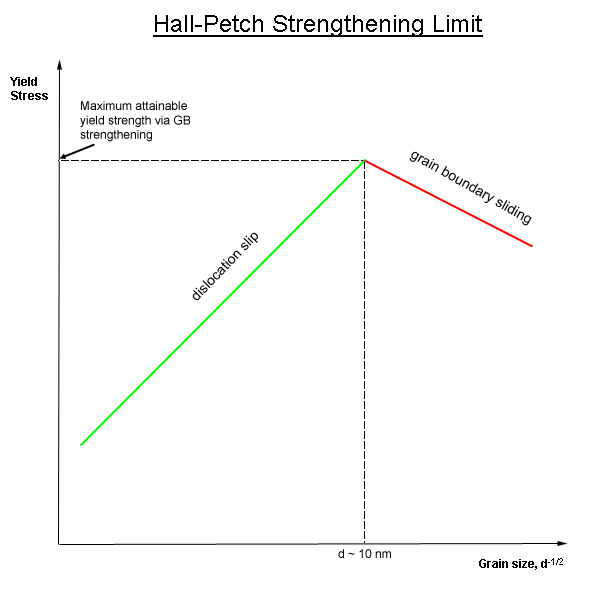


Grain Boundary Strengthening Wikipedia
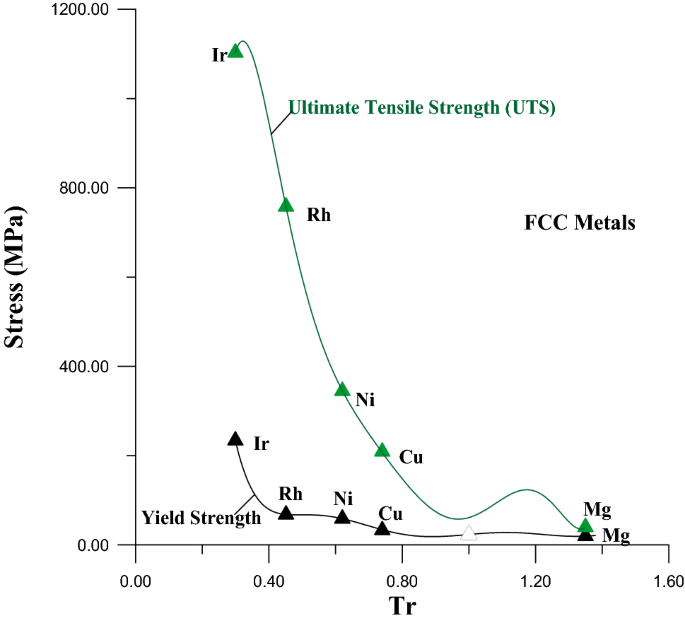


Estimation Of The Ultimate Tensile Strength And Yield Strength For The Pure Metals And Alloys By Using The Acoustic Wave Properties Scientific Reports



Isbt212 04 3 Stress And Strain Proportional Limit And Yield Strength Youtube


Engineering Stress Strain Curve



Strength At Break Tensile



How To Find Yield Strength Quora
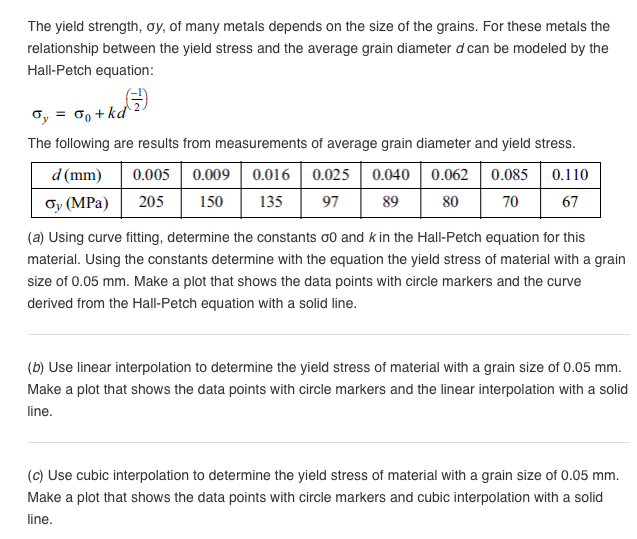


The Yield Strength Oy Of Many Metals Depends On Chegg Com


Scaling Equation For Yield Strength Of Nanoporous Open Cell Foams Unt Digital Library


Solved The Stress Strain Curve For A Bone Is Shown In The Chegg Com



How To Design For Stiffness Using Material Properties Fictiv



What Is Tensile Testing Instron
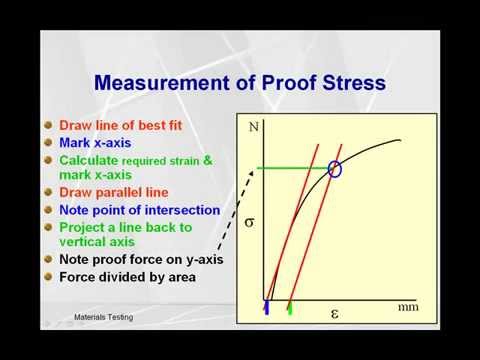


Calculate Proof Stress Youtube
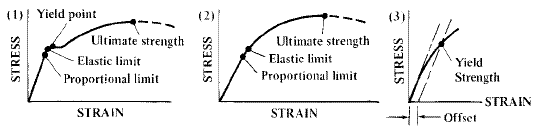


Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


Correlation Between Engineering Stress Strain And True Stress Strain Curve
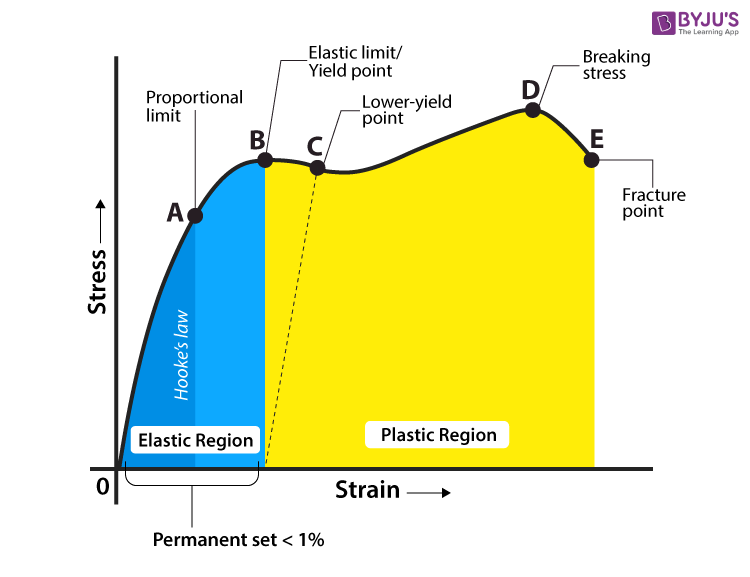


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



What Is The Von Mises Stress And The Yield Criterion



Stress And Strain Mechanical Properties Of Materials


Stress Strain Tensile Stress Tensile Strain Elastic Strain Energy Breaking Stress Plastic Brittle


Basic Of Drillpipe Tensile Capacity And Its Calculation Drilling Formulas And Drilling Calculations



How To Find Yield Strain Corresponding To 0 2 Offset Yield Stress


Solved Hi I Am Trying To Solve Q4 Below But I Don T Und Chegg Com



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia


コメント
コメントを投稿